Description
Introduction
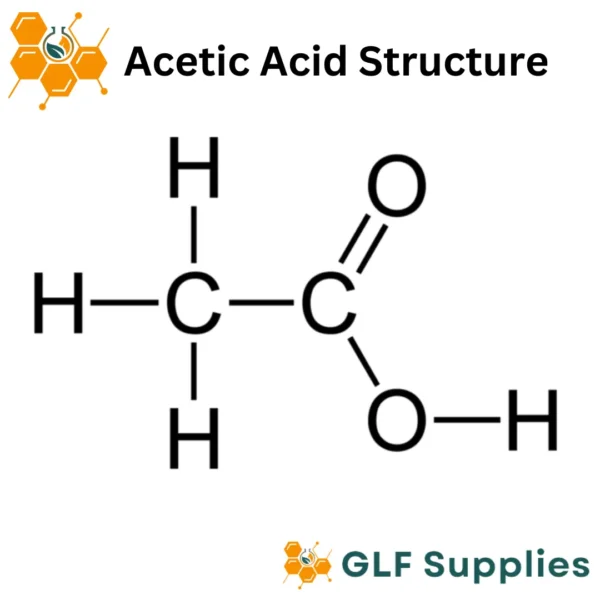
Acetic Acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is an organic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent smell and is a crucial component of vinegar. Acetic Acid is produced through the fermentation of ethanol by acetic acid bacteria or via chemical synthesis.
INCI Name :
Acetic Acid
IUPAC Name :
Acetic Acid
Other Names :
Vinegar (when dilute), Hydrogen acetate, Methanecarboxylic acid, Ethylic acid.
Formula :
CH3COOH
CAS No:
64-19-7
E number 260
Derived from :
Air oxidation of acetaldehyde, by oxidation of ethanol (ethyl alcohol), and by oxidation of butane and butene.
Solubility :
Acetic acid is infinitely miscible in water, also miscible with alcohol, glycerol, ether, carbon tetrachloride. It is practically insoluble in carbon disulfide.
Certified & Safety Rating :
EWG 1
Uses
Acetic Acid finds numerous applications across various industries due to its versatile properties some of them are as follows:-
Pharmaceuticals:
It is used in certain medicinal formulations and pharmaceutical processes.
Food and Beverage Industry:
It is a primary constituent of vinegar, adding a distinct tangy flavor to foods and serving as a natural preservative in pickling processes.
Cosmetics and Personal Care:
Acetic Acid is used to control the pH of cosmetics and personal care products. Vinegar is used in the formulation of hair conditioners, shampoos, hair rinses, wave sets, and can be found in skin care products.
Cleaning Products:
Acetic Acid is employed as a cleaning agent for surfaces like glass, tiles, and countertops, effectively dissolving mineral deposits and stains.
Textile Industry:
It is utilized in dyeing processes to fix dyes on fabrics, making them more colorfast.
Chemical Industry:
Acetic Acid is a vital raw material for the production of various chemicals, including acetic anhydride, acetate esters, and synthetic fibers like acetate rayon.
Organic Synthesis:
It serves as a versatile building block in organic synthesis, playing a crucial role in the creation of various chemical compounds.
Laboratory Uses:
Acetic Acid is commonly used in laboratories as a solvent and reagent in chemical reactions.
Precautions
While Acetic Acid is generally recognized as safe for its intended applications, it is a corrosive substance and should be handled with caution. Direct contact with concentrated Acetic Acid can cause skin and eye irritation, and inhalation of its vapors may cause respiratory discomfort. Proper safety measures, such as using protective equipment and working in well-ventilated areas, should be observed during handling.
In summary, Acetic Acid’s versatility and extensive range of applications make it an indispensable organic acid in numerous industries, contributing to the production of chemicals, food preservation, cleaning, and organic synthesis, among other uses. When used responsibly and with appropriate precautions, Acetic Acid proves to be a valuable and reliable compound in various industrial and domestic applications.